On December 5th, Amazon released AmazonGo to shock the industry. Lei Feng.. first studied the patent documents and interviewed senior computer vision algorithm engineers. Finally, he published two patent documents and gave a glimpse of what black technology is hidden in AmazonGo?
Today, Lei Feng.com interviewed the unmanned retail store entrepreneur Chen Weilong to explain AmazonGo and unmanned retail store projects in more detail. Chen Weilong graduated from Zhongshan University and has personally participated in and implemented many similar unmanned retail solution systems. He has deep knowledge and practical experience in the whole process flow system.
AmazonGo system composition
Chen Weilong “splits†the AmazonGo system into three parts: people/shelves/imports. The hardware and software components are organized as follows:

The layout is as shown below:
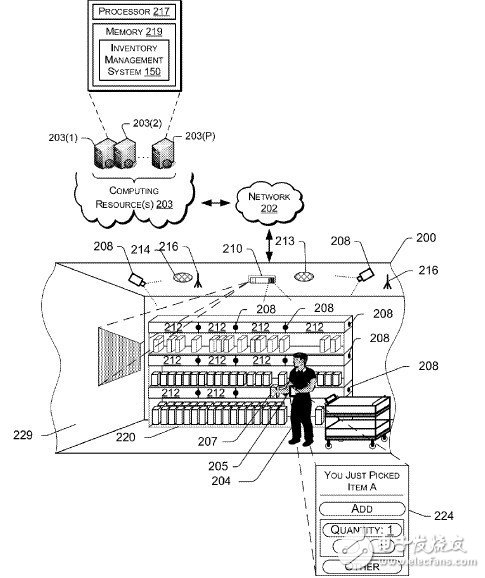
Multiple cameras are mounted on the shelf walls, and multiple sensors are buried at the bottom or top of each shelf. The camera is responsible for taking pictures, and the light curtain/infrared sensor is responsible for creating a horizontal plane. If the user's hand passes through this surface, the user starts to perform some kind of action and improves the efficiency of image analysis. Pressure/infrared sensors are used to indicate the location and status of an item, providing data for the user's behavior.
Use these data for deep learning, establish a commodity-action-human discriminant model, and improve the system's anti-cheat/recognition ability.
What is the core technology of AmazonGo?
Chen Weilong revealed to Lei Feng that the core technology of AmazonGo is anti-cheat/identification system. No matter how powerful business functions it provides, as an unmanned supermarket system, anti-cheat/recognition is the first element of its existence.
In existing supermarkets, it is legal to identify customer behavior through plainclothes patrols and surveillance cameras, such as placing them in shopping bags/cars or in clothes, standardizing the user's behavior to a specified range, and finally identifying the goods and customers through the cashier. Corresponding relationship, successfully solved who did what to do, and thus concluded the transaction.
Among them, civil air defense and air defense are anti-cheating systems, which are responsible for explaining customer behavior, thus ensuring the relationship between goods and customers, while the cashier is responsible for confirming the relationship between goods and customers. In AmazonGo, the system also has to solve the problem of who is doing what.
The next content is divided into big three, to explain how Amazon Go does.
First, how to detect and identify customer behavior: take or put back?
Chen Weilong pointed out that customers' shopping behavior is very rich. From the perspective of the shelf, the core actions can only be taken or returned.

In any case, the goods are taken away from the shelf, the biggest possibility is that they are bought, and you are not needed when you are released. If you can identify the take away or put it back, then the core problem is solved. According to the AmazonGo patent, it does this:
Capture the image of the user's hand before entering the shelf plane.
Capture the image of the user's hand after leaving the shelf plane.
In contrast, you can know whether to take out the goods or put them in the goods.
If it is picked up, the features of the hand before entering and the hand after entering and the items in the hand are distinguishable. This feature is opposite to the insertion. Simply put, if it is picked up, the hand is empty before entering, there is no commodity, and there are items in the hand after leaving. Put it in the opposite direction. So how do you identify your hand? It can be distinguished from the shape and picture color (skin tone). Using the light curtain or infrared to form a plane in front of the shelf, you can know that the user's hand is there.
In addition to image analysis, sensors can also provide such data. A combination of multiple data can be used to determine whether the user's behavior is taken or put back.
Second, how to accurately identify the items that were taken away and the items that were returned?
We know that with the action of the customer, we must also identify the goods that the action bears, or the phenomenon of Zhang Guan Li Dai will appear. Chen Weilong continued to explain that this part is divided into two steps: identifying the items that were taken away and identifying the items that were returned.
Identify the items that were taken away
Because the item is manually placed by the employee, the item can be tagged directly into the system, so there is no need to identify what the item is (it has been manually identified). Use the sensor to indicate that it was taken away.
In some cases, the item may not be set up or set up and then confusing, then the image is required to identify whether the existing item at the location is consistent with the item that should be. For example, item A is placed in item B, and if it is handled only in the manner mentioned above, it will be treated as item B, but this is less.
If it is a high confidence event, you can directly confirm, update (increase) the list of items, otherwise there will be a link for customer collaboration confirmation.
Identify the items that were returned
Before the item is returned, the relationship between the user and the item can be determined by the list of items, and the pictures of the items are stored in the system.
Retrieve the image and compare it with the item being placed to identify the item.
High confidence can be used to judge the item correctly, update (delete) the item list, otherwise there will be a customer collaboration confirmation link.
The items that are put back will have a misplaced position, and the employee will be notified after the identification.
Whether it is taken or put back, if it is a low confidence event, it will be recorded and analyzed by the system.
For normal shopping, the types of goods in the fixed area are single and easy to identify. For items that are misplaced, the difficulty and the amount of calculation will not increase significantly because the probability is less. However, for deliberate cheating, great computing resource identification is required. This issue is discussed later.

3. Who is the person who performed a certain action on a certain product?
According to the data, AmazonGo has set up a “transfer zone†in the import and export, similar to the anti-theft door of the existing supermarket. This door can scan the user's QR code to identify the import and export customers. Chen Weilong explained that the key to the problem here is that AmazonGo needs to identify in real time who the person who performed an action on a certain product is.
From the problem, we can find that the key to solving this problem is to start on the shelf, because anyone must implement the action on the goods before the shelf. With regard to this part of the details, the AmazonGo patent gives an explanation that uses user location information to identify it.
For example, Zhang San stood in front of the shelf A. At this time, the A shelf goods were taken away, then it was determined that Zhang San purchased the goods. There is a big hidden danger here is the problem of Zhang Guan Li Dai, because the customer is only positioned by location, as long as the users in this area may be regarded as buyers, thus forming a one-to-man relationship between goods and customers. If the location location area is limited to a sufficiently small area, a one-to-one correspondence can be achieved.
Image analysis and audio analysis used by AmazonGo. The camera detects the user and its position, and multiple audios in the ceiling or shelf can analyze the user's position based on the time difference. In addition, the antenna on the ceiling can be triangulated to determine the position, and the user's mobile phone GPS can also provide positioning.
Regarding indoor positioning or crowded area positioning, general positioning technology cannot be solved. At present, there are GPS in foreign countries that are positioned to the millimeter level, but the cost is extremely high and the application is rare. iBeacon technology can also be used for indoor positioning, up to the centimeter level, but limited to IOS devices.
In general, the AmazonGo anti-cheat/recognition system operates through the “Commodity-Recognition Action—Identify Goods Subject to Action—Commodity and User List/User Associationâ€.
For the Amazon Go anti-cheat/identification system, it only needs to know which items have been taken or put back, and who knows who implemented it, then know who bought/returned what items. Finally, in the exit (transfer area), the customer swipes the card to confirm the relationship between the customer and the product.
Discussion on commodity identification
At this point, there is a question: deliberate cheating can recognize the action, but it is difficult to identify the product, because there are 100,000 kinds of products in the supermarket, which cannot be solved according to the existing level.
Chen Weilong gave the following solutions to this problem:
Limit specific types of goods. From the official Amazon video, we can see that the types of supermarket products are much smaller than those of daily life supermarkets, and the shape specifications are relatively uniform.
Limit the opening area and crowds. In the mid-to-high-end market, users have higher credibility and less anti-theft pressure in supermarkets. The products displayed in the video also tend to the mid-to-high end market.
Special crowd tracking. The above-mentioned actions to improve user behavior that are determined by the system to be low confidence are tracked and analyzed, and this part of the population requires separate technical limitations and manual intervention.
Tolerate cheating and strengthen non-technical anti-cheating methods. Although the discussion is about high-tech content, it is better to mention the necessary artificial means at the current stage.
POWER UNITS FOR METALLOGRAPHIC INLAY MACHINE
Hydraulic Power Unit For Melting Equipment,Load Holding Hydraulic Valve,Electric Hydraulic Valve Body,Hydraulic Pump Unit
CHANGZHOU ROHN HYDRAULIC SCI-TECH CO.,LTD , https://www.rohnhydraulic.com