With the development of society and modern technology, the Internet of Things has surpassed and has attracted the attention of many countries and people. The Internet of Things is based on the existing Internet. In addition to converged networks, RFID technology, and information technology, it also introduces wireless, which makes the M2M IoT deeper, and wireless sensor technology combines embedded systems. Technology, sensor technology, modern networks and wireless communication technologies, so it is also a hot research area. Today we will come to understand the wireless sensor network.

The Wireless Sensor Network (WSN) is a distributed sensing network with a sensor that senses and examines the outside world. The sensors in the WSN communicate wirelessly, so the network settings are flexible, the device location can be changed at any time, and the Internet can be connected in a wired or wireless manner. A multi-hop self-organizing network formed by wireless communication.
Wireless sensor network structure
Wireless sensor network systems typically include a sensor node, a sink node, and a management node.
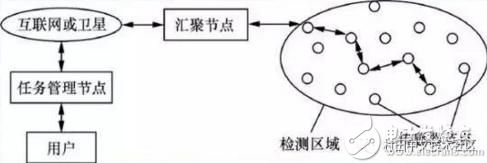
A large number of sensor nodes are randomly deployed in or near the monitoring area, and can form a network through self-organization. The data detected by the sensor node is transmitted one by one along other sensor nodes. During the transmission process, the detected data may be processed by multiple nodes, routed to the aggregation node after multiple hops, and finally reaches the management node through the Internet or satellite. The user configures and manages the sensor network through the management node and issues monitoring data.
Sensor Networks
Processing power, storage capacity, and communication capabilities are weak, and are powered by small-capacity batteries. From the perspective of network function, in addition to local information collection and data processing, each sensor node stores, manages, and integrates data forwarded by other nodes, and cooperates with other nodes to accomplish certain tasks.
Aggregation node
The aggregation node has relatively strong processing, storage, and communication capabilities. It is a gateway that connects the sensor network to the external network of the Internet, and implements conversion between the two protocols. At the same time, it issues monitoring tasks from the management node to the sensor node and puts the WSN. The collected data is forwarded to the external network.
Management node
The management node is used to dynamically manage the entire wireless sensor network. The owner of the sensor network accesses the resources of the wireless sensor network through the management node.
Main features of wireless sensor networks
Massive
In order to obtain accurate information, a large number of sensor nodes are usually deployed in the monitoring area, which may reach tens of thousands or even more. The large-scale nature of the sensor network includes two aspects: on the one hand, the sensor nodes are distributed in a large geographical area, such as using a sensor network for forest fire prevention and environmental monitoring in the original large forest, and a large number of sensor nodes need to be deployed; In terms of sensor nodes, the sensor nodes are densely deployed, and a large number of sensor nodes are densely deployed in a small space.
The large-scale nature of the sensor network has the following advantages: the information obtained through different spatial perspectives has a larger signal-to-noise ratio; the distributed processing of a large amount of collected information can improve the accuracy of monitoring and reduce the accuracy requirements for a single node sensor; The existence of redundant nodes makes the system have strong fault tolerance performance; a large number of nodes can increase the coverage of the monitoring area and reduce the cave or blind area.
Self-organizing
In sensor network applications, sensor nodes are usually placed in places where there is no infrastructure. The location of sensor nodes cannot be accurately set in advance. The mutual neighbor relationship between nodes is not known in advance. For example, a large number of sensor nodes are broadcasted by aircraft. In an extensive virgin forest, or randomly placed in an unreachable or dangerous area. In this way, the sensor node is required to have self-organizing capability, can be automatically configured and managed, and automatically form a multi-hop wireless network system for forwarding monitoring data through a topology control mechanism and a network protocol.
During the use of the sensor network, some sensor nodes fail due to energy exhaustion or environmental factors, and some nodes are added to the network to compensate for the failed nodes and increase the monitoring accuracy, so that the number of nodes in the sensor network is dynamically increased. Or reduce so that the topology of the network changes dynamically. The self-organization of the sensor network should be able to adapt to the dynamic changes of this network topology.
Dynamic
The topology of the network may change due to the following factors:
1 sensor node failure or failure caused by environmental factors or exhausted power;
2 changes in environmental conditions may cause changes in the bandwidth of the wireless communication link, even when the time is off;
3 Sensors, sensing objects and observers of the sensor network may be mobile;
4 new nodes are added. This requires the sensor network system to be able to adapt to this change, with dynamic system reconfigurability.
reliability
WSN is particularly suitable for deployment in harsh environments or areas unsuitable for humans. Nodes may be exposed to the open air, exposed to the sun, wind, rain, and even human or animal damage. Sensor nodes are often deployed in random, such as by aircraft or by launching projectiles to a designated area for deployment. These require the sensor nodes to be very rugged, not easily damaged, and adapt to a variety of harsh environmental conditions.
Due to the limitations of the monitoring area environment and the large number of sensor nodes, it is impossible to manually "take care of" each sensor node, and the maintenance of the network is very difficult or even impossible to maintain. The confidentiality and security of the communication of the sensor network is also very important. It is necessary to prevent the monitoring data from being stolen and the forged monitoring information. Therefore, the hardware and software of the sensor network must be robust and fault tolerant.
Data centered
The Internet is a computer terminal system, and then interconnected into a network, the terminal system can exist independently from the network. In the Internet, network devices are identified by a unique IP address in the network. Resource location and information transmission depend on the IP addresses of network devices such as terminals, routers, and servers. If you want to access resources on the Internet, you first need to know the server IP address where the resource is stored. It can be said that the existing Internet is an address-centric network.
The sensor network is a mission-based network, and there is no point in talking about sensor nodes out of the sensor network. Nodes in the sensor network are identified by node numbers. Whether the node number requires the entire network depends only on the design of the network communication protocol. Since the sensor nodes are randomly deployed, the relationship between the constructed sensor network and the node number is completely dynamic, and the node number is not necessarily related to the node position. When a user queries a event using a sensor network, the event of interest is directly advertised to the network instead of being advertised to a node with a certain number. The network reports to the user after obtaining the information of the specified event. This idea of ​​using the data itself as a query or transmission clue is closer to the habit of natural language communication. So usually the sensor network is a data-centric network.
For example, in a sensor network applied to target tracking, the tracking target may appear anywhere, and the user interested in the target only cares about the location and time of the target, and does not care which node monitors the target. In fact, in the process of moving the target, it is necessary to provide the location message of the target by different nodes.
Wireless sensor network security issues
Secure routing
Generally, in wireless sensor networks, a large number of sensor nodes are densely distributed in one area, messages may need to pass through several nodes to reach the destination, and the sensor network has dynamic and multi-hop structure, requiring each node to have routing function. . Since each node is a potential routing node, it is more vulnerable to attacks and makes the network insecure. The network layer routing protocol considers that the entire wireless sensor network provides critical routing services, and the secure routing algorithm directly affects the security and availability of wireless sensors. Secure routing protocols generally use link layer encryption and authentication, multi-path routing, identity serious, two-way connection authentication, and authentication broadcast mechanisms to effectively improve the network's ability to withstand external attacks and enhance routing security.
Security Protocol
In terms of security, there are two main methods: key management and secure multicast.
Key management: Wireless sensor networks have many limitations, such as node capacity limitations, which allow them to use only symmetric keys and technology; power capacity limitations should minimize communication in wireless sensor networks because communication consumes more power than Calculated power consumption; sensor networks should also consider aggregation and other issues that reduce data redundancy. In the deployment of the node money, the key is first configured in the node. Usually, the pre-configured key scheme calculates the session key through the pre-stored secret information. The pre-configured key management scheme must save storage space due to node storage and energy limitation. And reduce communication overhead.
Secure communication: Wireless sensor networks may be set up in hostile environments. In order to prevent suppliers from injecting fake information into the network, secure multicast based on source authentication is required in the wireless sensor network.
Exhaust Fuel Pressure Sensor,Pressure Transducer,Water Pressure Sensor,Waterproof Pressure Sensor
Shenzhen Ever-smart Sensor Technology Co., LTD , https://www.fluhandy.com