This article will discuss the specific process of supporting Layer 2 switch forwarding in VLANs. Through the combination of graphics and texts, understand the concrete manifestation of frames in the 802.1Q document of VLAN protocol.
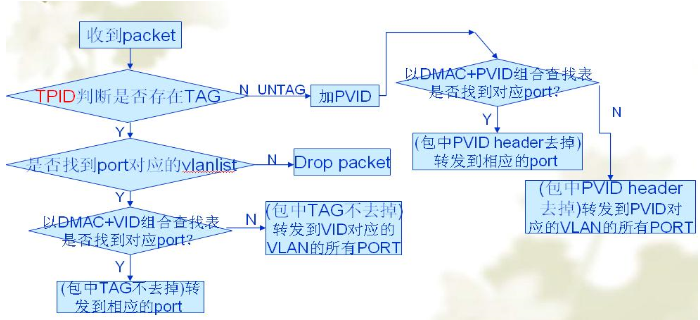
The above figure is the specific forwarding process of the Layer 2 switch. The following is a detailed description of the above figure.
First, let's take a look at what TPID means.
The frame in the 802.1Q document of the VLAN protocol is embodied in the following figure:
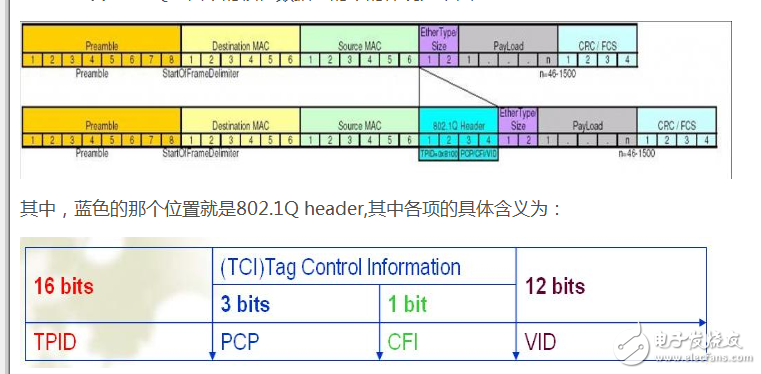
Tag Protocol IdenTIfier (TPID) : A set of 16-bit fields whose values ​​are set at 0x8100 to identify an IEEE 802.1Q frame as being tagged, and the field is calibrated. The same as the Ethernet format/length in the field of the unlabeled frame, this is used to distinguish unlabeled frames. By determining whether the value of this item is 0x8100, it can be determined whether the frame is a frame of a VLAN.
Priority Code Point (PCP): A set of 3-bit fields is used as a reference for IEEE 802.1p priority, from 0 (lowest) to 7 (highest), used to prioritize data streams. level.
Canonical Format Indicator (CFI): A 1-bit field. If the value of this field is 1, the MAC address is a non-standard format; if it is 0, it is the standard format; in the Ethernet switch, it usually defaults to 0. In Ether and Token Ring, CFI is used as a compatibility between the two. If the frame receives data in the Ethernet terminal, the value of CFI must be set to 1, and this port cannot be bridged with other ports that are not tagged.
VLAN IdenTIfier (VID): A 12-bit field that specifies which specific VLAN a frame belongs to. A value of 0 indicates that the frame does not belong to any of the VLANs; in this case, the 802.1Q tag represents priority. The value of 16-bit 0, 1, 0xFFF is reserved, and other values ​​can be used as identifiers of less than 4094 VLANs. This entry indicates the value of the VLAN ID.
Second, let's take a look at the entries of the switch table that supports VLANs:
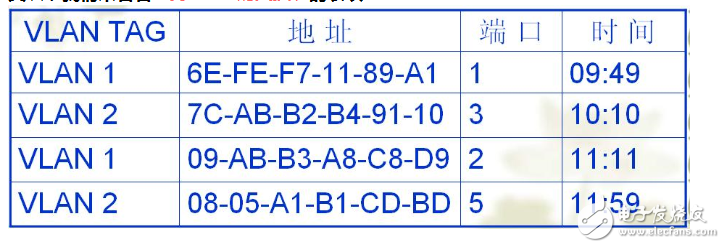
When vlan switch finds the switch table, it uses Dmac+vlanid as the key to search for the corresponding port number. Of course, this table can be self-learning like a normal switch.
Finally, other abbreviations are explained:
PVID: When a port receives an UNTAGED data frame, it cannot determine which VLAN to exchange. The PVID defines the VLAN in which the frame is exchanged in this case. In a sense, PVID can be understood as the default VLAN of the port.
TAGED: If the attribute of a port in a VLAN is TAG, then the data frame forwarded from the port is TAGED. (Of course, the data frame is exchanged in this VLAN)
UNTAGED: If the attribute of a port in a VLAN is UNTAG, then the data frame forwarded from the port is UNTAGED, but the PVID must be added to the switch before forwarding, so that it can be When a TAGED packet has a corresponding table, its packet is forwarded.
Poly Solar Panel,Solar Panel Module,Polycrystalline Solar Panel,Poly Crystal Solar Panels
Wuxi Sunket New Energy Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.sunketsolar.com