Global Information Grid Communication Capability Modeling
The Global Information Grid (GIG) is a military electronic information system created by the US military and is the foundation of future network-centric warfare. In-depth study of the global information grid is of great significance to improving our military's informatization level and advancing the new military revolution with information technology revolution as the mainstay. Starting with the concept, development plan, and architecture of the global information grid, focusing on the research of GIG communication capacity building, in-depth analysis of the GIG communication architecture reference model, and comparing with the traditional 0SI model; research on GIG communication infrastructure construction and communication Information security construction. Finally, it gives some enlightenments from GIG to the construction of military informatization.
Keywords: GIG; military informatization; communication capabilities; OSI
O Introduction The Global Information Grid (GIG) is a very large-scale information system that works on a global scale and is the product of a new era, new strategy, and new ideas. It can provide a set of value-added functions to support information processing, storage and transmission, and realize the optimization of human-network interaction, network management, information distribution management, information assurance and other functions. It is the trend of future distributed computer technology development. In the military field, the global information grid integrates the existing various information resources by transforming the existing "chimney" system to form an interconnected and interoperable network that can realize multi-dimensional information of "land, sea, air, and sky". The modern information warfare network that integrates "sensor network, computer network, and weapon platform network" has laid a solid foundation for winning the future information warfare.
l Global information grid development planning and system construction
1.1 GIG development plan In May 1999, the US Department of Defense released version 8.0 of the National Defense Information Infrastructure Master Plan-Realizing GIG, and proposed a complete plan for the construction of GIG. In June 2001, the US Department of Defense published The Network Center Warfare Report proposes a plan to build a global information grid network. According to the plan, the global information grid will be implemented in three stages: at the current stage, it is to integrate existing networks and processing facilities, establish an integrated information environment that connects the various services and the existing systems of the headquarters, and initially form a conceptual blueprint for the integrated system architecture In 2010, a blueprint for the future global system architecture of the global information grid was initially established, and it had initial operational capabilities; GIG was fully completed in 2020, with on-demand information bandwidth allocation, automatic information management, and end-to-end comprehensive interoperability.
1.2 Construction of GIG architecture The architecture is the basic framework of the system. It stipulates the system's composition principles, components, and the relationship between the activities of various parts and the way to achieve these relationships. GIG is a large-scale system, including all military-specific and leased communication and computing systems, as well as various software, data, applications, services and confidential services of these systems. GIG's structural framework is divided into 5 layers, as shown in Figure 1.

The design and development of the GIG architecture is based on communications and computer systems. The goal is to integrate various information with different architectures within the Department of Defense into a system with a single architecture to solve the integration and interoperability of various information systems The problem. The GIG architecture can be described from three perspectives: operational view, system view, and technical view. The brief relationship between the three architectures of operations, systems, and technology views is shown in Figure 2.
1.2.1 Operational view GIG's operational view describes the implementation of a specific concept in a specific context, providing the necessary operational elements, tasks, activities and information flow for the operation. It has 7 functions: information transmission, information storage, information processing, human-GIG interaction, network management, information distribution management and information security guarantee.
1.2.2 System view The system view can describe the system and the connection relationship required to realize the functional requirements of support and support operations. For a single system, the system view includes physical connections, locations, and identification of key nodes, circuits, networks, combat platforms, etc., specifying the performance parameters of the system and its components. For a domain, the system view illustrates how multiple systems are connected and interoperable, as well as the internal structure and operation of specific subsystems.
1.2.3 Technology view GIG's technology view adopts a joint technology architecture. The technology view is mainly a set of minimum rules that deal with the arrangement, interaction and interdependence of various components. The technical view provides guidelines for the realization of various technical systems. Under this guideline, engineering specifications are formulated, universal building blocks are built, and production lines are established.
2 Global Information Grid Communication Capacity Building Communication capacity building is intended to create an integrated communication network to provide warfighters with a stable, dynamic, and flexible information enterprise environment. Every resource in the battlefield space is connectable and capable of generating, processing, or transmitting information. The ground, airborne, and maritime communications components all use clearly defined and interoperable protocols and interfaces to achieve effective data exchange at the tactical level, dynamic information sharing at the operational level, and flexible decision-making and distribution at the strategic level.
2.1 Reference Model of GIG Communication System The reference model of GIG communication architecture is proposed based on OSI model and TCP / IP model, which is mainly divided into 7 layers, as shown in Figure 3. The physical layer, data link layer and network layer are communication subnets, which are closely related to data movement. The service layer and application layer are resource subnets, which are mainly involved in data processing in the network. The transport layer is located between the resource subnet and the communication subnet, and is the bridge between the communication subnet and the resource subnet. The mission layer is unique to GIG, and is required for military missions. It is a collection of specific applications. Each layer of the GIG communication system model is responsible for a specific job, and then transmits the data to the next layer. The characteristics of the GIG communication architecture reference model and the OSI reference model are compared in Table 1.
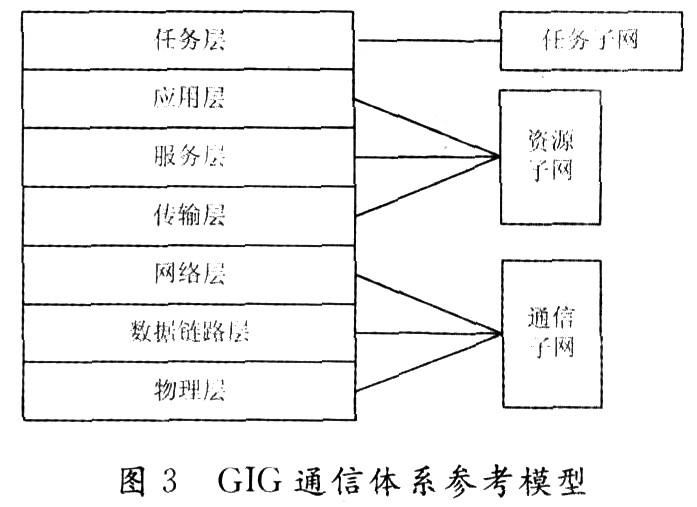

The physical layer is the lowest layer of the GIG communication system reference model and the foundation of the entire open system. The physical layer provides transmission media and interconnected devices for data communication between devices, and provides a reliable environmental foundation for data transmission. The unit of data transmission in the physical layer is bits.
The data link layer solves the communication problem between two adjacent nodes and realizes the transmission of error-free protocol data units on the links between two adjacent nodes. The protocol data unit transmitted by the data link layer is called a data frame.
The highest layer of the communication subnet at the network layer is related to the operation control of the communication subnet and embodies the way in which the resource subnet accesses the communication subnet in the network application environment. The main task of the network layer is to try to transfer the data packets from the source node to the destination node, so as to provide the most basic end-to-end data transmission service to the transport layer.
The transport layer is responsible for the highest layer of data communication. The task is to make the best use of network resources according to the characteristics of the communication subnet. It provides the functions of establishing, maintaining and canceling the transmission connection between the service layers of the two end systems. Reliable data transmission at the end. At this layer, the protocol data units for information transfer are called segments or messages.
The service layer organizes the communication between two session processes and manages the exchange of data. It handles the representation of information exchanged in two communication systems and provides a mapping from the Internet to IP addresses.
The application layer provides general-purpose and task-specific applications. It determines the nature of communication between processes to meet user needs. It not only provides the information exchange and remote operation required by the application, but also serves as the user agent of the application to complete some functions necessary for information exchange.
The task layer provides a collection of specific application programs from the application layer that are necessary to complete a specific military mission. The functions of the mission layer are: to convert the data transmitted by the application layer into useful information for use by weapon systems or networked combat personnel; decompose the combat mission into several specific steps, determine the applications required to complete these specific steps; notify the application The application program that the layer user wants to call, and complete the call in the order of execution.
2.2 GIG communication infrastructure construction Make full use of the characteristics of the existing architecture to achieve system compatibility, scalability and interoperability, so that it can not only adapt to the existing information environment, but also allow the embedding of new technologies.
According to the joint transformation roadmap of the US Department of Defense in January 2004, the communications infrastructure is mainly constructed in three parts: the ground segment, the wireless or radio segment, and the air-based segment.
(1) Ground segment construction Based on optical fiber technology, it mainly includes the GIG bandwidth expansion (GIG ~ BE) plan. It is mainly used to increase the transmission capacity of the busiest part of the US Department of Defense's existing communication network, and to provide greater bandwidth and high survivability for major military computer centers worldwide. The existing GIG bandwidth extension technologies of the US military mainly include dense wavelength division multiplexing technology, the use of commercially mature technologies at the data link layer and network layer, the use of MPLS at the network layer to establish virtual private networks and complete encryption functions, Compatible with the original network system, laser communication technology, deployment of broadband Internet, etc. In December 2005, the United States Defense Information System Agency (IUSA) announced that GIG-BE has achieved full combat capability, using OC-192 (10 Gb / s) information to connect more than 100 backbone nodes in the DISN at high speed. By 2010, it is expected to launch 1,700 broadband terminals that can be used. The instantaneous exchangeable bandwidth it can provide is 4.875 GHz, and the transmission capacity is 1.2 to 3.6 Gb / s.
(2) Wireless or radio section construction The wireless or radio section construction will be based on a programmable, modular joint tactical radio system (JTRS), with the ability to receive and transmit multiple waveforms and network connection protocols used in the RF spectrum, which can be Combatants provide vertical and horizontal network connections within the RF spectrum, and provide voice, video, and data services to echelon commanders at all levels. In February 2006, the United States JTRS Joint Plan Executive Office changed the equipment form originally divided by "cluster" into "region", which is initially divided into: ground area, airborne and maritime area, network enterprise area and dedicated radio area.
(3) Construction of the air base section The air base section will be based on the laser technology of broadband communication satellites, which can provide greatly improved communication capabilities and integration based on Internet protocols, and multi-sectoral network connection capabilities to achieve aerial and aerial information, surveillance and Global real-time connection of reconnaissance data. The US military plans to upgrade and replace the existing communication satellite system in the next 5 to 10 years. Replace the DSCS III with broadband supplementary satellites, replace the UFO system with the mobile user target system, and replace the Milstar system with an advanced extremely high frequency system.
2.3 Construction of communication information security Security and confidentiality are related to the success or failure of GIG technology. The same information is intercepted and used by enemy forces, which will bring a heavy blow to our army and even determine the victory or defeat of the war. For this reason, as early as 2001, the US National Defense Science Board (DSB) submitted a report on "Homeland Defense-Defensive Information Warfare" to the US Department of Defense, which pointed out the implementation plan for GIG's information assurance. At present, the main technologies of communication information security construction are virtual private network (VPN) and defense-in-depth strategy (DID).
(1) Virtual private network A virtual private network is a collection of multiple geographically dispersed sites connected by a communication network. The use of multi-protocol identification switching (MPLS) technology to establish independent VPNs, each VPN is only logically isolated from each other, the information on a VPN cannot be viewed and changed by users in other VPNs, so the VPN ensures that its information is in Logical privacy.
(2) In-depth defense strategy The core idea of ​​in-depth defense is to configure, maintain, and monitor information security facilities at multiple levels such as GIG's host, network, and support infrastructure, to protect information and information systems against cyber attacks, and to enable intruders to break through One layer of defense meets another layer of defense immediately. The defense-in-depth strategy combines various effective defense methods, so that the various defense methods can make up for each other's weaknesses, to resist various attack methods, and seek the most reliable protection for the information.
3 GIG's enlightenment on the informatization of our army
3.1 From the operational requirements, strengthen the research on the architecture. The technology has been constantly changing as the needs change, drawing on the successful experience of the US GIG development, and starting from the analysis of operational requirements, to build a communications system architecture suitable for our army. Based on operational requirements, the developed products are more targeted. The development of information technology has changed the basic laws of traditional wars. The core elements of warfare, such as the center of gravity of operations and the concentration of forces, have changed. Wars have appeared in a disorderly and non-linear form. Fully understand the actual combat requirements and existing problems, strengthen the research on the architecture, and lay a good architectural framework for the top-level design of the communication system.
3.2 Take the road of combining military-civilian communications construction to improve our military's communications infrastructure construction capabilities Compared with the US military, our military's communications infrastructure construction is relatively weak, and various dedicated networks cannot achieve effective interconnection, interoperability, and combat Command platforms, sensor platforms, and shooter platforms cannot yet be seamlessly connected. Therefore, we must accelerate the construction of our military ’s communications infrastructure. However, if we want to do a good job of communication infrastructure construction, we must take the road of combining military and civilian communications, connecting military and civilian communications forces and various parts of communication facilities into an organic whole, and forming a mechanism for the coordinated development of military and civilian communications. Reduce costs and improve military communication capabilities efficiently, not only can quickly establish a military communication network covering the world and three-dimensional deployment, but also can effectively use military communication network resources to support national economic construction and achieve overall optimization of civilian communication and military communication. the goal of.
3.3 Raise the awareness of information security and strengthen the security construction of our military's communication network The traditional military communication network is simpler and less interconnected. Therefore, more research is focused on information security technology. In the future, military communication networks are much more complicated, and the stronger the dependence of war on information systems, the more important the issue of communication network security becomes. Through the understanding and research on the information security of the communication network of the U.S. military GIG system, combined with the actual situation, we will strengthen the construction of our military communication network security.
4 Conclusion The future war will inevitably be an information-based and network-based war. The information on the battlefield is constantly changing. Anyone who can grasp the information in time will be able to master the initiative of the war. GIG is proposed on the basis of the realization of network-centric warfare. It is The key to winning the future information warfare. Through in-depth research on the construction of global information grid communication capabilities, this article hopes to provide some reference and help for the transformation of our military's military informatization from platform central station to network central station.
Gesture control
Smoke sensor
Auto cleaning
Sensor touch control
Energy saving
Top Mounted Range Hood Black,Silence Range Hood,Powerful Range Hood,Automatic Range Hoods
JOYOUNG COMPANY LIMITED , https://www.globaljoyoung.com