The battle between ARM and Intel processor architectures continues to heat up. Intel's x86 status is indeed unshakable today, but ARM has significant power consumption advantages and will be more attractive in the future. So what kind of CPU can best meet the future needs?
ARM released the Cortex-A15 processor in 2011, which uses a multi-core disordered superscalar design with a main frequency of up to 2.5GHz. Cortex-A15 is of great significance because it runs counter to the previous generation ARM design. The previous generation ARM processor achieved the lowest energy consumption at the expense of performance. On the contrary, the Cortex-A15 has a clear goal of achieving powerful performance indicators, while placing low energy consumption in a secondary position. ARM Holdings is essentially an intellectual property company that issues its own design licenses to other manufacturers. The manufacturer manufactures the chip, and then applies the chip to other manufacturers' system products. At the end of 2012, Cortex-A15-designed products began to appear on the market, and more such products are expected to appear in 2013.
However, ARM is not the only processor company that wants to win future competition. A few weeks ago, Intel released a new low-power CPU based on its own Atom architecture for the data center. The Atom S1200 series is designed to provide x86 instruction set compatibility on low-power SoCs. Atom S1200 series is mainly aimed at micro servers and other performance-oriented applications with low power consumption.
The following is a brief comparison of Samsung Exynos5250 (authorized implementation of the recently launched Cortex-A15) and Intel Atom S1260 (a high-end product of the S1200 series). Exynos5 series is used in the latest SamsungGoogle Chromebook and Nexus10 tablet. It should be noted that the two processors of Samsung Exynos5250 and Intel Atom S1260 are only in the huge processor family, so the best optimization for one market is not completely suitable for another market. The most typical example is Exynos' 4GB memory limit, which is normal for mobile applications, but obviously not suitable for cloud computing. However, the Cortex-A15 architecture uses a 40-bit paging memory algorithm ("large physical address extension") that can support up to 1TB of memory.
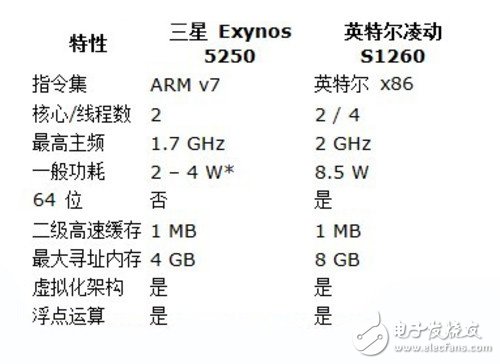
Note: The power consumption of Exynos5250 is currently unknown and difficult to obtain. I searched all the Samsung documents and I couldn't find them. My only gain is to find the voltage estimate at StreamCompuTIng. This value may not be correct. The main purpose here is to show that its power consumption is quite low, which may be lower than Atom 1260.
The question now is which ARM or Intel x86 CPU is better? However, this will raise another question: in what way is it better? The two markets that Leverhawk is mainly interested in are mobile computing and cloud computing, so subsequent analysis will also focus more on these two aspects.
The main factors to be compared include:
Power consumption
performance
Application compatibility
Data center features
Lithium Battery Charger,Oem Psp Pro Charger,Lithium Ion Battery Charger,Lithium Ion Battery Charging
Ninghai Yingjiao Electrical Co., Ltd. , https://www.yingjiaoadapter.com